Disaster response Open database
1. Introduction
- Brief overview of the importance of data in disaster response
- Explanation of the concept of open data and its relevance to disaster response
2. Key Areas of Data Needs for Disaster Response
- Energy and Water Procurement
- Types of energy and water needed during disasters (e.g., generators, fuel, bottled water)
- Sources of supply (e.g., manufacturers, distributors, emergency stockpiles) * Corrected to add a specific example of "emergency stockpiles" *
- Prosthesis and Assistive Devices
- Types of assistive devices needed for disaster victims (e.g., prosthetic limbs, wheelchairs)
- Availability of specialised equipment and expertise
- Repair and Spare Parts for Manufacturing of Machinery
- Types of machinery used in disaster response (e.g., heavy equipment, medical equipment)
- Sources of spare parts and repair services
- Big Small Scale of Protective Bio-Hazard Equipment
- Types of protective equipment needed for bio-hazards (e.g., PPE, decontamination supplies)
- Availability and manufacturing of specialised equipment and expertise
3: Database Structure
- Manufacturing Locations
- Geographical coordinates and locations of manufacturing facilities
- Types of products manufactured at each location
- Manufacturing Equipment
- Types of equipment used in production (e.g., 3D printers, machining tools)
- Availability of spare parts and maintenance services
4: Benefits of Open Data in Disaster Response
- Improved Situational Awareness
- Access to accurate and timely data enables more effective decision-making during disasters.
- Enhanced Collaboration
- Sharing of open data fosters cooperation among stakeholders, including governments, NGOs, and private sector entities.
5. MVP
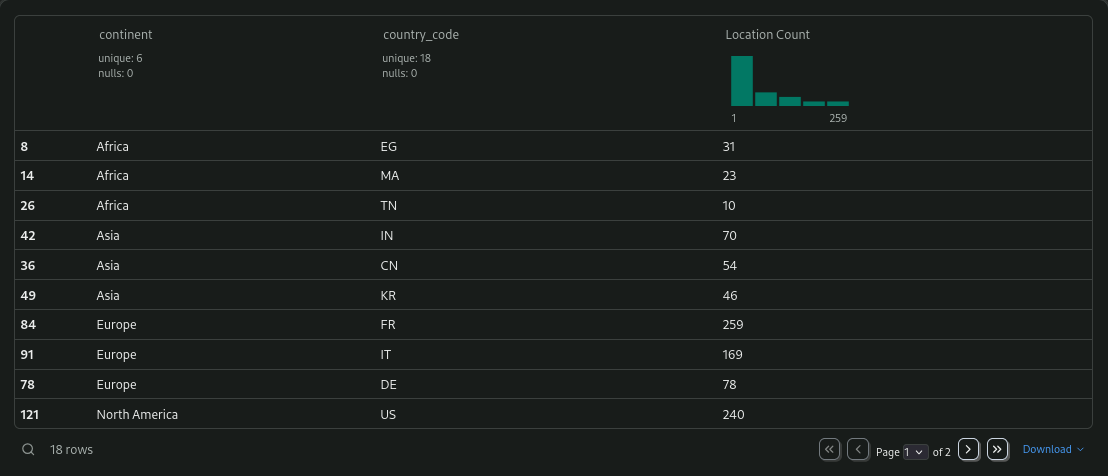
- Make a test run for the regions of Egypt and France.
- Create an scenario where a pandemic has strike and items are needed in hospitals.
- Base on the interaction study from Hackaday Prize and other research UI determine the actions and functions to gather:
- A Portable document holding manufacturing product intelligence. (Product A)
- Data of locations.
- Maker/Fab Repairing spaces.
- Machining services.
- Catalogue of machines and quantities.
- Skilled people. (Skills)
- Catalogue of Projects/Products made/deployed in the area.
- Repairing spaces.
- Map visualisation tool: Kepler.Gl
- with a data analysis and data resume.
- Data of locations.
- A brief guideline on how to use the data. (Product B)
- A database setup and forms for the collection of new data. (Product C)
- A Portable document holding manufacturing product intelligence. (Product A)
Current challenges:
Get African Makers to engage and participate.
